When it comes to funding businesses, Venture Capitalist (VC) and Private Equity (PE) are two major players that dominate the landscape. Although both investors infuse capital into companies with high growth potential, their strategies approaches, and target companies often differ significantly.
Venture Capital – The Early Believers and Backers
Venture capital firms are the early believers and backers of tomorrow’s giants. They invest in early-stage companies that exhibit a high growth potential but are often too risky for traditional banks and have limited access to other fundraising mechanisms. These firms become involved in the life of a start-up as early as the Series A financing round, providing not just funding but often strategic guidance and networking opportunities.
Private Equity – The Heavyweight Division
In contrast to venture capitalists, private equity firms tend to step in at a later stage in a company’s life cycle. PE firms typically seek out companies with a minimum of around $5 million in revenue. These businesses are more mature than venture-stage companies and are often looking for capital to fuel significant expansion, or they may need a strategic partner to navigate a pivot or turnaround.
The intersection of VC and PE
Both VC and PE firms raise funds from limited partners (LPs) like pension funds, endowment funds, and wealthy individuals. They promise these LPs attractive returns within a 5 to 7-year window, which is considered the typical lifespan of a fund before it seeks to liquidate its holdings for returns.
Choosing the Right Investment Path
Cremades advises entrepreneurs to recognize the stage their company is at before engaging with either VCs or PE firms. If you’re a start-up in the early stages, your sights should be set on venture capital. If your company has a substantial revenue base and you are considering larger, more strategic maneuvers, then private equity could be the appropriate path.
Key Differences between Venture Capital and Private Equity
1. Investment Stage
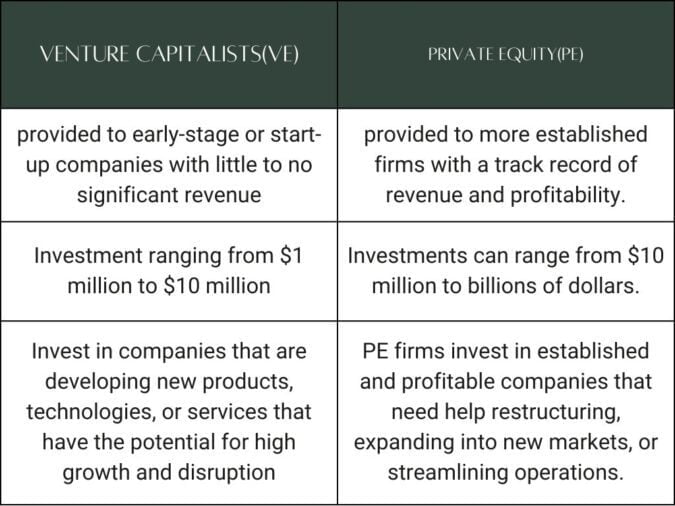
One of the primary differences between VC and PE is the stage of investment. VC is typically provided to early-stage or start-up companies with little to no significant revenue, while PE is provided to more established firms with a track record of revenue and profitability.
2. Investment Amount
Another difference is the investment amount. VC investments are typically smaller than PE investments, with the average VC investment ranging from $1 million to $10 million while PE investments can range from $10 million to billions of dollars.
3. Investment Focus
VC and PE firms also have different investment focuses. VC firms invest in companies that are developing new products, technologies, or services that have the potential for high growth and disruption. In contrast, PE firms invest in established and profitable companies that need help restructuring, expanding into new markets, or streamlining operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between VC and PE can save entrepreneurs time and resources while seeking funding, and align their businesses with the right kind of investors who not only provide capital but also align with their long-term goals and growth strategies.

